- Welcome to : Locus Health Centre
- Welcome To Locus Health Centre
We try to post the most common conditions we interact with so you are familiar with what are some of the conditions we can help you with.

What is PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
➢ Plantar fasciitis is an overuse condition resulting in inflammation of the plantar fascia.
➢ The cause of plantar fasciitis is overuse due to overtraining, poor technique, running on hard surfaces or prolonged standing and activities such as running and dancing.
The symptoms often occur after a major or rapid adjustment to a training program.
➢ Some of the predisposing factors are improper footwear that is worn out and weight gain including pregnancy.
➢ Most common cause of foot pain in athletes (ex. Runners).
➢ People with plantar fasciitis are usually over 40 years of age. However, very active athletes may experience symptoms at as early as 20 years of age.

What is COMPARTMENT SYNDROME?
➢ A compartment syndrome (Anterior (front), Lateral (side) and Posterior (back)) is the result of an increase in pressure within the compartments of the lower leg.
While any of the compartments can be affected, the anterior compartment is most prone at 45% of cases.
➢ Another term for chronic compartment syndrome is “CHRONIC EXERTIONAL COMPARTMENT” SYNDROME.br>
➢ The causes of compartment syndrome IF ACUTE are trauma such as a direct blow to the compartment and due to overuse and if it is CHRONIC would be due to overtraining, poor technique or training on hard surfaces.
➢ The predisposing factors are muscle type involved in creating a muscle imbalance, muscle tightness and improper footwear that is worn out, too flexible, too stiff or does not provide adequate arch support.
➢ PIt usually occurs in athletes under 40 years of age.
What is MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS (Golfer’s Elbow)?
➢ A medial epicondylitis is inflammation of the common flexor tendon (CFT) that results to microscopic tearing of tendon fascicles due to overloading the tendon with a resulting inflammatory response.
➢ The causes of lateral epicondylitis are repetitive activities, muscle imbalance, poor techniques on sports/activities and lack of flexibility.
➢ It is common to sports like golfing, throwing and racquet sports and occupations such as construction, plumbing or carpentry.
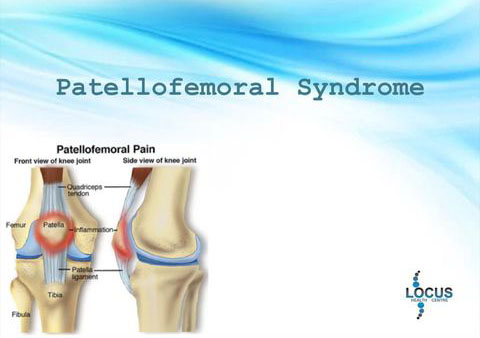
What is PATELLOFEMORAL SYNDROME?
➢ Patellofemoral syndrome describes various painful degenerative changes to the articular cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap). It is also called Patellofemoral Tracking Disorder.
➢ The contributing factors that cause patellofemoral syndrome are abnormal biomechanics, knee injury, repeated knee stress and overuse, tight muscles like quadriceps (Vastus lateralis), hamstrings and calf muscles (
gastrocnemius), weak muscles such as glutes (Gluteus medius) and quadriceps (Vastus medialis) and arthroscopic procedures.
➢ It affects the general population more specifically adolescents, young active adults and elite athletes. It is also common to people who are into running sports and cycling.
What is ILIOTIBIAL BAND CONTRACTURE AND FRICTION SYNDROME?
➢ Iliotibial band contracture is a contracture or thickening of the iliotibial band.
➢ Iliotibial band friction syndrome is inflammation and pain where the iliotibial band crosses the lateral femoral condyle.
➢ The causes of iliotibial band contracture are activities or occupations that place the knee and hip in flexion such as cycling, horseback riding, prolonged sitting, running and prolonged wheelchair use or bedrest.
➢ The causes of iliotibial band friction syndrome are prolonged, repetitive activities such as running and cycling.
➢ It is a common injury to active individuals or athletes that are into activities such as cycling and running
What is LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS?
➢ A lateral epicondylitis is inflammation of the common extensor tendon (CET) that results to microscopic tearing of tendon fascicles due to overloading the tendon with a resulting inflammatory response.
➢ The causes of lateral epicondylitis are repetitive activities such as hammering, using a screwdriver and playing tennis.
➢ It is common to racquet sport players especially novice players with poor backhand stroke, wheelchair athletes, plumbers and meat cutters.

What is a Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)?
➢ A whiplash is an acceleration-deceleration injury to the head and neck combined with its collection of symptoms that are affecting the neck that are caused by the accident.
➢ The cause of whiplash is an acceleration-deceleration of the head and neck relative to the body, usually resulting from vehicular collision but also possible in contact or high-speed sports.
➢ A contributing factor to the accident itself may be active trigger points (“knots”) of one of the neck muscles. These result in dizziness when a person rotates his head quickly, as when making a s
houlder check while driving. This dizziness can be dangerous as it may cause the driver to lose control of the vehicle.
➢ More severe and long-lasting symptoms result from rear-impact collisions than from front or side impact.
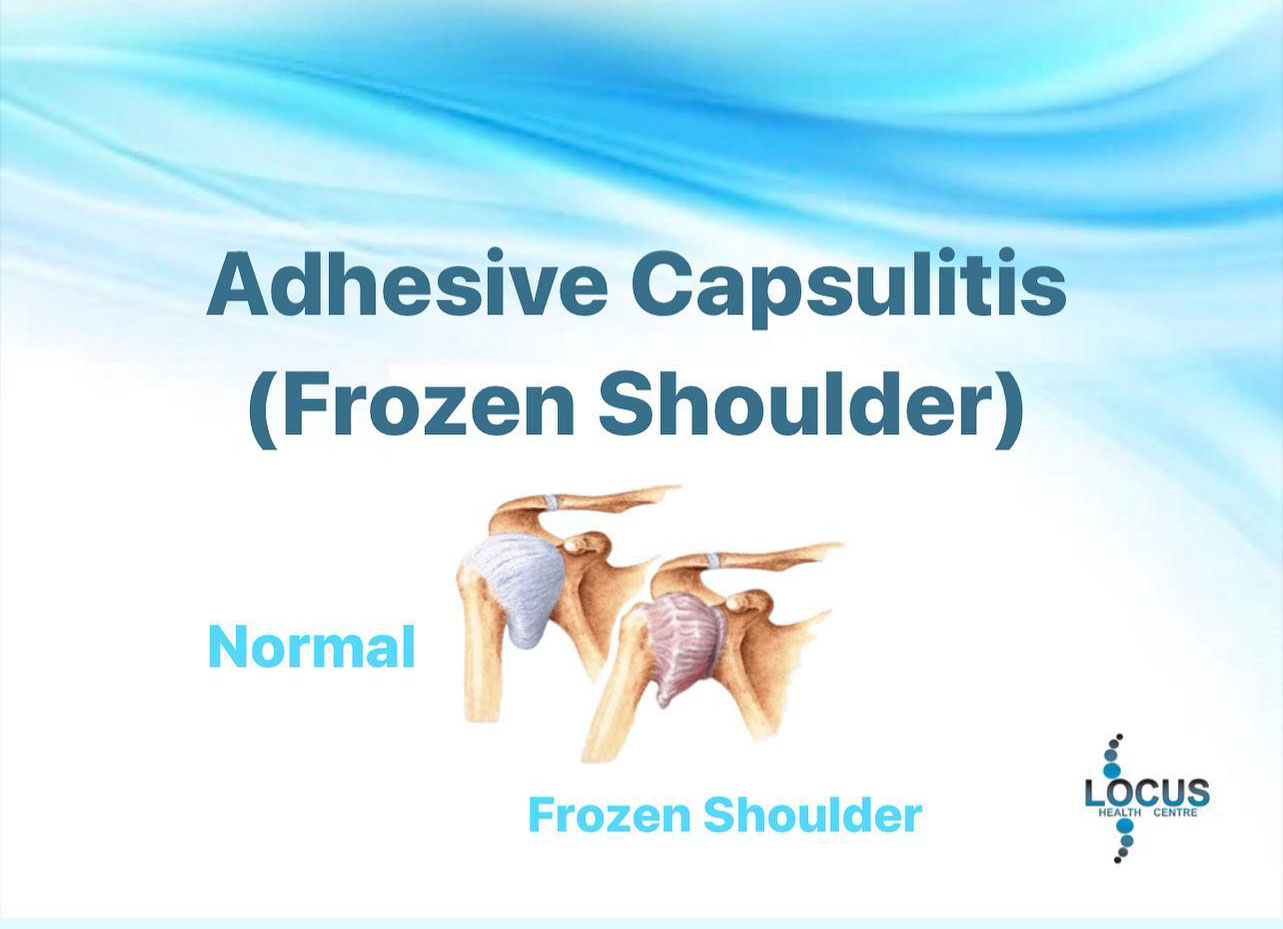
What is FROZEN SHOULDER?
➢ Frozen shoulder is painful, significant restriction of active and passive range of motion at the shoulder, most frequently in abduction and external rotation.
➢ The causes of frozen shoulder are musculoskeletal trauma or disorders such as impingement syndrome, subacromial bursitis, rotator cuff tendinitis, dislocations, osteoarthritis or gout,
trigger points (“knots”) in subscapularis muscle, postural dysfunction such as head-forward posture, immobilization following shoulder injury, systemic diseases such as diabetes and hyperthyroidism.
➢ 2-3% of the population may experience this condition, which affects more women than men.
➢ Frozen shoulder rarely occurs in those under 40 or over 70 years of age.
Copyright © 2022. Locus Health Centre. All Rights Reserved